Last Sunday (January 5), the Wuhan Municipal Health Commission confirmed 59 cases of unexplained viral pneumonia in Wuhan City. All patients were quarantined and there were no deaths reported. There was no proof of human-to-human transmission, but it could be due to a new coronavirus, the virus family that triggered the deadly outbreaks of SARS and MERS, World Health Organization (WHO) said on Wednesday (January 8).
WHO Risk Assessment and Advice
The symptoms reported were fever, with a few patients having difficulty in breathing, and chest radiographs showing invasive lesions of both lungs. WHO advised that public health measures and surveillance can refer to Infection Prevention and Control Guideline. Under the Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) section, appropriate use of PPE served to reduce the risks of transmission of respiratory pathogens.
Strengthen Outbreak Management and Emergency Response Systems
As a deadly epidemic outbreak such as the Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) crisis has shown, an infectious disease could spread far in a matter of days without national borders. Although improving the country-level first line of defense is the cornerstone of the global health risk system, enhancing international capacity for preparedness, alertness, and response to outbreaks is a second vital component.
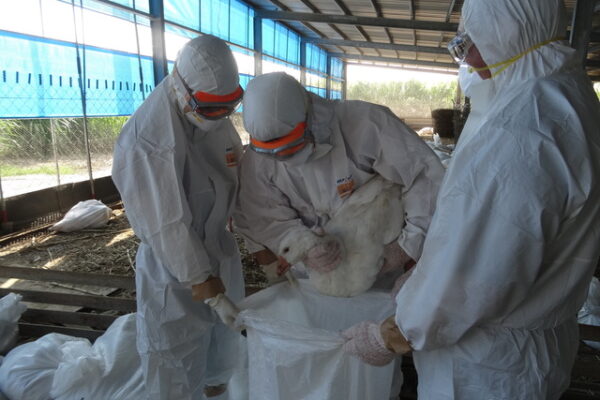
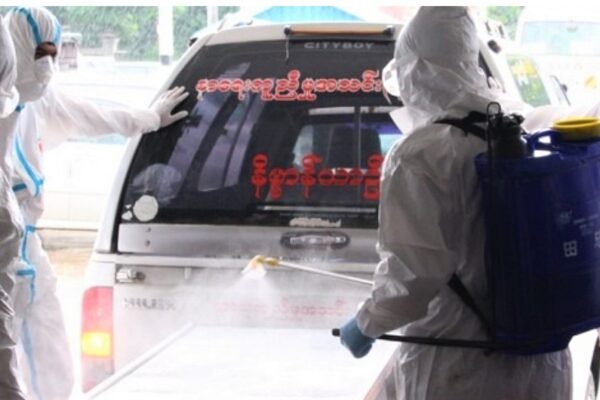
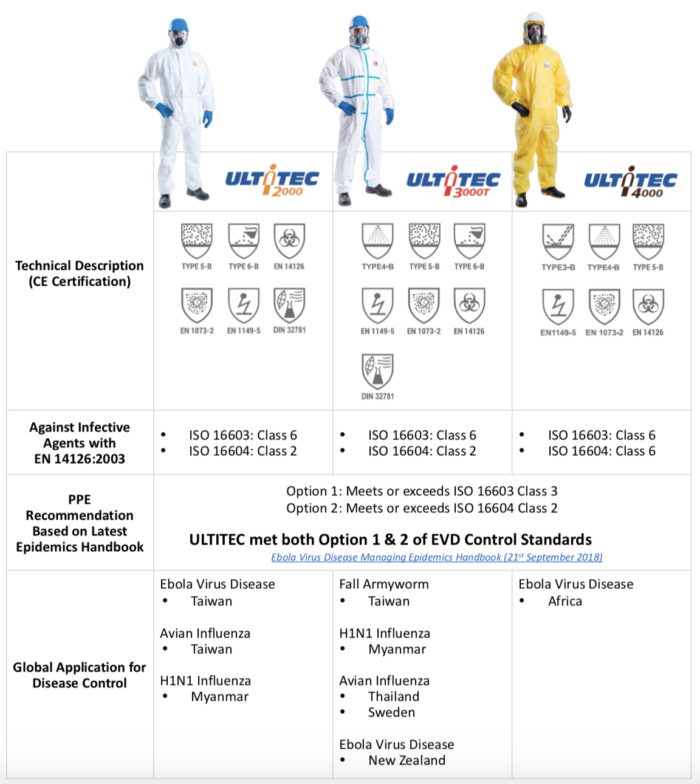
ULTITEC offers Type 3 to Type 6 protective clothing certified by the latest PPE Regulation (EU) 2016/425, namely ULTITEC 2000, ULTITEC 3000T, and ULTITEC 4000. ULTITEC was selected to provide ultimate protection for frontline operators during the recent global disease control and management, namely EVD (Africa, New Zealand), H1N1 (Myanmar), and Avian Influenza (Taiwan, Thailand, Sweden).
(Left) ULTITEC 2000 and ULTITEC 3000T being applied during Myanmar H1N1 disinfection / XYZ News
(Right) Frontline operators wore ULTITEC 2000 for Taiwan Avian Influenza culling operation / The Central News Agency