Why is it important to protect your skin?
Many chemicals used in the workplace might cause diseases by affecting or passing through the skin. The skin is our body’s largest organ. It serves as a shield against potentially dangerous things. The outside surface (epidermis) serves as the primary protective layer, and the inner surface (dermis) serves as the second protective layer (dermis).
On the other hand, human skin is not a perfect barrier. There are still many chemicals that can harm us if they get into our bodies. The level of moisture in your skin is also a factor to consider. When the epidermis’ moisture content is too high or too low, it can compromise the skin’s barrier. Skin that has been dehydrated can become rough, thickened, and flaky, losing its suppleness. When skin becomes too moist, however, it weakens its barrier function.
As a result, the purpose of wearing Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is not only to keep chemicals from encountering your skin but also to keep moisture between the skin to prevent the epidermis from losing its ability to protect itself.
What health problems can occur through skin contact?
The chemical problems affecting the skin may be roughly divided into 4 substances: irritants, burns, allergic, and diseases.
- Irritants: An irritant is a rash that is red and itchy and is caused by direct contact with a harmful substance. It is a skin reaction that causes inflammation on the skin’s surface. Swelling, flaking, blistering, cracking, and pain may occur as a result. The inflammation is usually a temporary symptom that goes away once the skin heals.
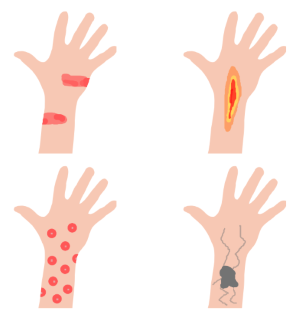
Pic 1: Health Problems of Skin
- Burns: Occur when the skin contact with strong chemicals such as acid, alkaline, or caustic based chemicals. The amount of skin damage depends on the strength of the chemical, how much of it was on the skin, and how long it was there. Even minor chemical burns can be excruciatingly painful.
- Allergic: Allergic contact dermatitis (also known as skin sensitization) is an immunological response. Your body’s immune system believes it is under attack and sends antibodies to help fight the invader. The reaction may appear itself not only on the contact skin but also in other parts of the body, such as a red rush, shortness of breath, or even a fatal reaction. However, once a person develops an allergy, even small amounts will set it off. By then, the only option is to avoid further exposure.
- Diseases: Many chemicals have been shown to cause occupational diseases when they pass through the skin and accumulate in the body. Examples include diseases of the kidneys (from carbon tetrachloride), heart (from carbon disulfide), blood (from benzene) and nervous system (from organophosphates). Some health effects appear quickly, while others take months or years to appear.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Skin problems and diseases have been the most common non-injury health issue. Wearing proper PPE is the primary solution to preventing or avoiding skin overexposure during work. The key categories of PPE include the head, eyes, hands, legs, feet, and bodies. The level of protection is proportional to the level of risk in the working environment. Body cover clothing, such as aprons, coveralls, and chemical suits, which are easily forgotten by workers are still required for many jobs.
To meet the protection level, the PPE was made of a variety of materials for skin protection. The wearer must not only select the appropriate level of PPE protection, but also properly wear and remove PPE. The risk of skin exposure increases if PPE is used incorrectly. For example, unfit PPE may leave some areas of the skin unprotected and directly exposed to harmful objects.

Pic 2: Use Appropriate PPE to Prevent Chemical Harms
PPE can only be effective if it is used correctly. Training in the use and limitations of PPE is required in the workplace, whether you are an employee, supervisor, or manager. The entire workplace must be trained in safety awareness. This includes the purpose of the PPE, how to use it, the risks it will avoid or limit, and actions to ensure it remains in good condition.
For example, if you work in a hazardous chemical environment, your PPE such as gloves and clothing must meet certain standards. First, know what chemicals you’re dealing with, and make sure your PPE is chemical-resistant. Then, check the datasheet to see if they have been tested and certified for chemical resistance. Additionally, the validity period must be checked to ensure that the PPE is still capable of providing protection. To put on the PPE, follow the instructions and checklist. The final step is to ensure that you can take off safely to avoid causing additional pollution to the environment.
Case Study
Hydrofluoric acid (HF) is a powerful inorganic acid that easily penetrates the skin layers, both epidermis and dermis, and into the bones. Fluoride ions are responsible for systemic poisoning and can cause tissue necrosis and bone destruction when they burn the skin. If the patient’s skin encounters HF without protection and immediate treatment, the wound can be fatal.
A young worker in the silicon wafer manufacturing industry received an HF burn because of an incorrect operating movement, and acid container splashes injured his leg. The worker wore neither chemical-resistant gloves nor protective clothing. Because of the pain in his leg, he is unable to reach the first aid station and wash the wound thoroughly with water.
In this case, the worker lacked sufficient safety awareness of the risk. He overestimated the level of protection in his workplace. We may be able to avoid a tragedy like this one if all workers are aware of the dangers they face and use the proper protective equipment, such as chemical-resistant gloves and clothing.
Conclusion
PPE for skin protection is something that every job that uses PPE should be aware of today. It does, however, have some limitations:
- it can only protect the wearer.
- it must be of the proper material and size.
- it must be put on, worn, and removed correctly.
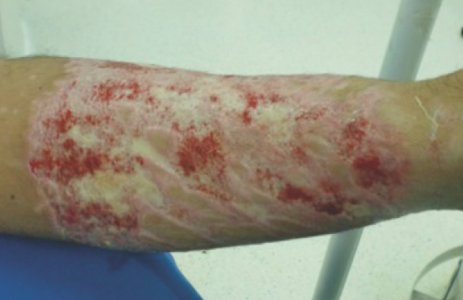
Pic 3: HF Chemical Burned Skin
When it comes to choosing PPE for skin protection, it is critical to properly train the wearer on when, where, and how to use this PPE. Too many people wear PPE incorrectly, which can pose a greater risk than not wearing it at all. Be sure you take the time to train your workers on how to use proper PPE to reduce risks in the workplace!

