What’s the meaning of Breathability?
When frontline operator chooses protective clothing, not only consider the garment protection level but also thinking about the comfortability. The comfortable garment makes the wearer willing to wear longer and extend protection for a longer time. There are many factors of protective clothing relate to comfortability. The most critical factor of comfortability is fabric breathability.
When we talk about the breathability of fabric, it usually means the ability of fabric to absorb and release moisture outward skin. It is the degree to which a fabric permits air or moisture to pass through. Therefore, the more breathable a fabric is, the greater moisture permeability it will have.
What are the benefits of breathable fabric as a protective clothing?
There are 3 ways that human body dissipate heat
- Moisture (Sweat) Evaporate. The heat is drawn away from the body with the vapor, leaving the skin surface cooler.
- Convection and conduction. The heat is lost to air or other materials that are in contact with the skin.
- Radiation. The heat is given off by infra-red(IR) radiation.

Pic 1. Body heats dissipate through fabric of protective clothing
The body heat may be blocked by the fabric of protective clothing. With a breathable fabric, the vaporized sweat may pass through the fabric easily and make skin dry and cool down. That’s the reason why moisture evaporate is the most efficient way to dissipate body heat.
On the other hand, the objective of protective clothing is to block the dangerous substance out of the garment, which includes liquid drops and vapors sometimes. The type of fabric for protective clothing may reduce the air permeability to increase the protection level on purpose, which causes the situation frontline operators hesitate to wear protective clothing. Therefore, choose protective clothing with breathable fabric is crucial for wearers, especially since the heavy workload may generate massive body heat.
How to measure breathability
Many test methods conduct to measure the transmission of water vapor through fabric material. All of them rely on creating a humidity gradient in the test system between two sides of the fabric. Breathability rating for fabric is generally measured by two indexes, Moisture Vapor Transmission Rate (MVTR) and Resistance of Evaporation of a Textile (Ret).
Moisture Vapor Transmission Rate (MVTR)
The value of breathability is calculated by measuring the amount of moisture vapor pass through the fabric and reported as the moisture vapor transmission rate (MVTR). Higher value indicates better removal of vapor and moisture. The MVTR is reported as gram per square meter (g/m2) during a specified period (usually 24hrs) under defined temperature and humidity.
The test method is to measure the weight change after a period of time. There are 2 kinds of method to measure the MVTR, Upright Cup Test and Inverted Cup Test. Also known as JIS L 1099, JIS Z 0208, ISO 2528, and ASTM E96.
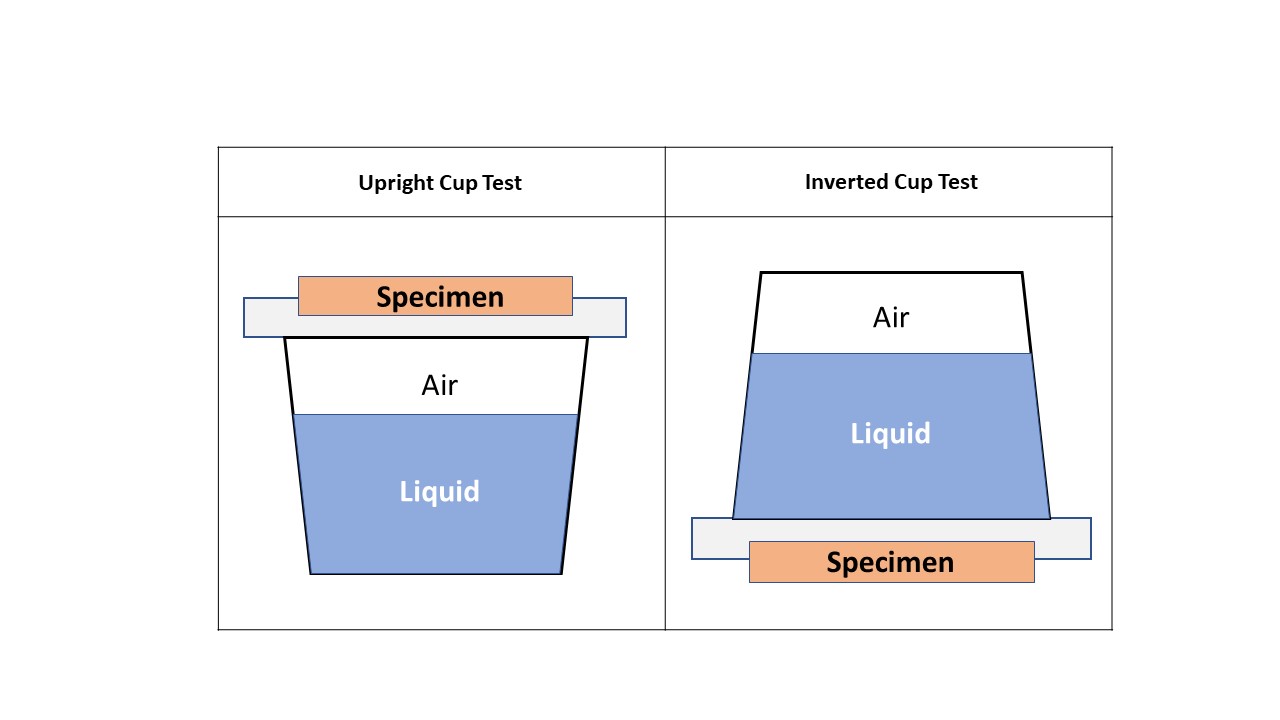
Table 1. MVTR test method
Resistance of Evaporation of a Textile (Ret)
The Ret test measures the evaporative resistance of the fabric under test and moisture loss when extra heat is applied on it. The resistance of evaporation of a textile refers to the level of resistance that a given fabric will demonstrate against evaporation, meaning that the lower the Ret value, the fabric has better breathability.
The Ret test method is slightly different from the MVTR test. Also known as ISO 11092 or Hohenstein test. The fabric is placed above a sintered metal plate, and heated water is channeled into the metal plate to simulate perspiration. Based on the Ret values of the fabric, they came up with a Comfort Rating System.
Comfort Rating System of Ret value
| 0 – 6 | Extremely breathable. Comfortable at a higher activity rate. |
| 6 – 13 | Good to very good breathability. Comfortable at moderate activity rate. |
| 13 – 20 | Satisfactory to acceptable breathability. Uncomfortable at a high activity rate. |
| 20 – 30 | Unsatisfactory or slightly breathable. Moderate comfort at a low activity rate. |
| 30 + | Unsatisfactory or not breathable. Uncomfortable and short tolerance time. |
Conclusion
When selecting protective clothing for frontline operators, not only the protection level, but also the breathability. Breathability is important for protective clothing in two ways. First, the breathable fabric allows vapor moisture diffused and prevent you from overheating during work duty.
Secondly, it allows air to pass through the fabric to keep comfort. The comfort of a fabric depends on its ability to transmit vapor moisture from the body to reduce the accumulation of water (sweat) on the skin. The less humidity inside the garment, the more comfortable you feel.
For the activities in a dangerous environment, you should not only choose an appropriate protection level of protective clothing, also need to consider the MVTR or Ret Value. Choose an appropriate protective clothing combined with both safety and breathability will make a huge difference during your job.

